As an educator, I’ve always been fascinated by the power of data in shaping student outcomes. The information we gather about our students can provide valuable insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and learning needs. In this article, I’ll be sharing some examples of student data that can help teachers make informed decisions and tailor their instruction to meet the unique needs of each learner. From standardized test scores to formative assessments and behavior records, these examples will demonstrate how data can be a powerful tool in driving student success.
One example of student data that can be incredibly informative is standardized test scores. These scores provide a snapshot of a student’s academic performance and can help identify areas where they may need additional support or enrichment. By analyzing these scores, teachers can gain a deeper understanding of their students’ strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to tailor their instruction accordingly.
Another example of student data that can be valuable is formative assessments. These ongoing assessments provide real-time feedback on student learning and can help teachers gauge their understanding of the material. By collecting and analyzing this data, educators can identify areas where students may be struggling and adjust their teaching strategies to better meet their needs.
Definition List For Examples of student data
As an experienced educator, I understand the importance of using data to inform instruction and support student success. In this section, I will provide you with a definition list of various examples of student data that can be used to gain insights into student learning and tailor instruction accordingly.

- Standardized Test Scores: These scores provide a standardized measure of a student’s academic performance in specific subjects, such as math, reading, or science. They can help educators identify areas where students may need additional support or enrichment.
- Formative Assessments: These assessments are conducted during the learning process to provide ongoing feedback on student understanding and progress. Examples include quizzes, exit tickets, and classroom observations. By using formative assessments, teachers can adjust instruction in real-time to meet the specific learning needs of students.
- Classroom Observations: This involves observing students in the classroom to gather data on their behavior, engagement, and learning strategies. It can provide insights into how students interact with the content and identify any patterns or misconceptions that need to be addressed.
- Attendance and Behavior Records: Monitoring student attendance and behavior records can give teachers a better understanding of the factors that may impact a student’s performance and well-being. This data can help identify potential barriers to learning and inform appropriate interventions.
- Student Work Samples and Portfolios: By examining student work samples and portfolios, educators can assess their progress over time and identify areas of growth or areas where additional support may be needed. These artifacts can provide a comprehensive picture of a student’s abilities and learning trajectory.
- Engagement Data: Tracking student engagement can provide valuable insights into their level of participation and interest in the classroom. This data can help teachers adjust instructional strategies and create a more engaging learning environment.
Remember, the key to leveraging student data effectively is to analyze it thoroughly and use it to inform instructional decisions. These examples of student data serve as valuable tools to better understand your students’ strengths, weaknesses, and learning needs. By utilizing these insights, you can tailor your instruction to meet the unique needs of each learner and drive student success.
Why Is Student Data Important?

As an experienced educator, I understand the significance of using data to inform instruction and support student success. By utilizing various examples of student data, teachers can gain valuable insights into student learning and tailor their instruction accordingly. Let’s explore why student data is so important:
Enhancing Student Learning
When we analyze student data, we can identify patterns and trends that give us a better understanding of our students’ unique strengths and weaknesses. This information allows us to design targeted interventions and strategies to support their individual learning needs. By tailoring our instruction based on data, we can create a more engaging and effective learning environment for all students.
Identifying Areas of Improvement
By examining student data, we can pinpoint specific areas where our students may be struggling. Whether it’s through standardized test scores, formative assessments, or classroom observations, data provides us with concrete evidence of areas that require additional attention. Armed with this information, we can develop targeted interventions and provide additional support to help our students overcome their challenges and achieve academic success.
Personalizing Education
Every student is unique, with their own learning preferences and needs. By using student data, we can personalize education and create individualized learning plans that cater to each student’s strengths and weaknesses. Whether it’s adjusting the pace of instruction, providing additional resources, or offering alternative methods of assessment, data allows us to tailor our teaching to meet the diverse needs of our students. This personalized approach fosters greater engagement, motivation, and ultimately, student success.
As educators, we have a responsibility to utilize student data effectively to drive instruction and support student success. By analyzing and utilizing data, we can gain insights into our students’ learning needs, identify areas for improvement, and personalize their education. With data as our compass, we can lead our students towards academic excellence and help them reach their full potential.
Types of Student Data
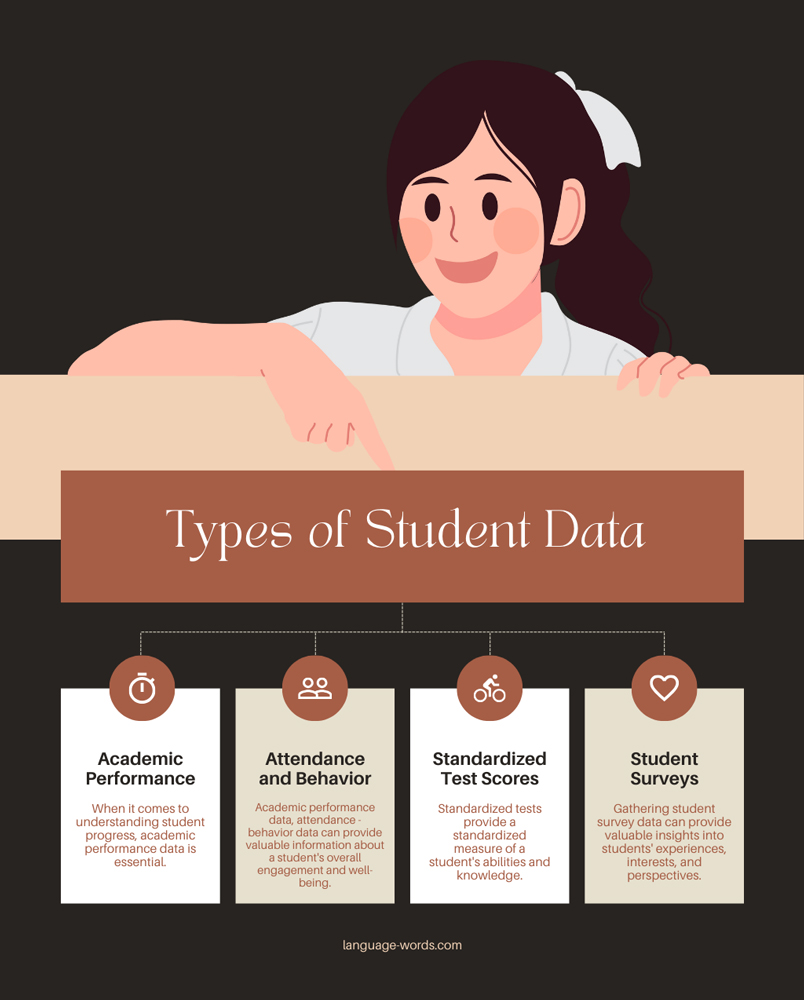
Academic Performance
When it comes to understanding student progress, academic performance data is essential. This data provides insights into how well students are mastering the curriculum and meeting learning objectives. Some examples of academic performance data include:
- Grades on assignments and tests
- Classwork and homework completion rates
- Progress in specific subjects or topics
By analyzing academic performance data, educators can identify areas where students excel and areas that may require additional support or intervention.
Attendance and Behavior
In addition to academic performance data, attendance and behavior data can provide valuable information about a student’s overall engagement and well-being. Examples of attendance and behavior data include:
- Daily attendance records
- Tardiness and absences
- Incidents of discipline or behavior referrals
This data helps educators identify patterns and trends that may impact a student’s ability to participate fully in their education. It also allows for early intervention and support for students who may be facing challenges.
Standardized Test Scores
Standardized tests provide a standardized measure of a student’s abilities and knowledge. Standardized test scores can offer insights into a student’s academic proficiency compared to their peers. Examples of standardized test scores include:
- State assessments
- National assessments
- College entrance exams
By analyzing standardized test scores, educators can assess the overall performance of their students and identify areas of strength and areas where improvement is needed.
Student Surveys
Gathering student survey data can provide valuable insights into students’ experiences, interests, and perspectives. Examples of student surveys include:
- Surveys about classroom culture and learning environment
- Surveys about their interests and preferred learning styles
- Surveys about their overall satisfaction with their educational experience
By collecting and analyzing student survey data, educators can gain a better understanding of their students’ needs and interests, allowing for more personalized and effective instruction.
Remember, the key to utilizing student data effectively is not just collecting it, but also analyzing and using it to inform instruction and support student success. These different types of student data provide a comprehensive picture of a student’s academic journey, allowing educators to tailor their approach to meet the diverse needs of every student.
Examples of Student Data Analysis

Tracking Academic Progress Over Time
When it comes to analyzing student data, one of the most valuable insights is tracking academic progress over time. By consistently monitoring academic performance data, educators can identify patterns and trends in student learning. This allows for targeted interventions and personalized instruction.
For example, let’s say I notice that a student’s reading comprehension scores have been steadily improving over the past few months. This data suggests that the strategies and interventions implemented are having a positive impact. On the other hand, if I see a decline in a student’s math scores, it can indicate the need for additional support or a change in instructional approach.
Identifying Students at Risk
Another critical aspect of student data analysis is identifying students who may be at risk academically or socially. Through the analysis of attendance and behavior data, educators can uncover trends that may indicate a need for intervention.
For instance, if I notice a student has been consistently absent, it may affect their academic progress. By identifying these attendance patterns early on, I can work with the student, their parents, and the school administration to find strategies to improve attendance and ensure their success.
Analyzing Learning Styles
Understanding the unique learning styles of students is essential for effective instruction. By analyzing student data, such as surveys or assessments that measure learning preferences, educators can gain valuable insights into how each student learns best.
For example, if I analyze survey data and discover that a student prefers visual learning, I can provide them with visual aids or graphic organizers to support their understanding. By adapting instructional practices to accommodate different learning styles, I can create a more inclusive and engaging learning environment.
Evaluating the Impact of Interventions
Lastly, analyzing student data is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or instructional strategies. By examining the data before and after implementing an intervention, educators can determine if it has had the desired impact on student learning.
For instance, if I implement a specific reading intervention and see a significant improvement in a student’s reading fluency scores, it indicates that the intervention is effective. On the other hand, if there is no change or a decline in performance, it may be necessary to adjust the intervention or explore other possibilities.
Analyzing student data provides valuable insights into academic progress, identifies students at risk, helps tailor instruction to different learning styles, and evaluates the impact of interventions. By utilizing these diverse types of student data effectively, educators can make informed decisions to support student success.
Ethical Considerations in Student Data Analysis

Protecting Student Privacy
When it comes to analyzing student data, it is of utmost importance to prioritize the privacy of our students. As an educator, I understand the sensitivity of the information we collect and the need to safeguard it. Here are some key considerations when it comes to protecting student privacy:
- Data anonymization: Before analyzing student data, it is crucial to remove any identifying information that could link the data back to individual students. This ensures that their privacy is protected.
- Secure data storage: Storing student data requires robust security measures. It is essential to use encrypted databases and secure servers to prevent unauthorized access. By taking these precautions, we can ensure that student information remains confidential.
- Limited access: Only authorized personnel should have access to student data. By restricting access to a select few individuals, we can reduce the risk of data breaches and maintain the privacy of our students.
Ensuring Data Security
In addition to protecting student privacy, it is equally important to ensure the security of the data itself. Data security involves safeguarding student information from unauthorized modification, disclosure, or destruction. Here are some measures to ensure data security:
- Strong password protection: Implementing strong password policies and encouraging regular password updates can help prevent unauthorized access to student data. It’s important to remind staff members to choose unique, complex passwords to enhance security.
- Regular data backups: Regularly backing up student data helps safeguard against accidental data loss or corruption. By having multiple copies of the data stored in secure locations, we can ensure its availability and recovery in case of unforeseen circumstances.
- Updates and patches: Keeping software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches is imperative to prevent vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers. Regularly installing updates helps ensure the security and integrity of student data.
Transparency and Consent
In the era of data-driven decision making, it is essential to be transparent about how we collect and use student data. Respecting the rights of students and their families is paramount. Here are some ways to promote transparency and obtain consent:
- Clear data policies: Clearly communicating our data policies to students and their families helps build trust and ensures they understand how their data will be used. Providing information about the purpose, methods, and security measures surrounding data analysis promotes transparency.
- Obtaining informed consent: Before collecting student data, obtaining informed consent from parents or guardians is vital. This ensures that families are aware of the data being collected, the purpose of its collection, and their rights regarding its use.
- Allowing for opt-outs: Some families may choose to opt out of certain data collection activities. It’s important to honor their choices and provide alternatives for those who prefer not to participate. Granting this option respects their privacy and beliefs.
By prioritizing student privacy, ensuring data security, and promoting transparency and consent, we can responsibly analyze student data to inform instruction and support student success. As an educator, these ethical considerations guide my actions and enable me to make informed decisions for the benefit of my students.
Conclusion
In this article, I have discussed the importance of utilizing various types of student data to inform instruction and promote student success. By analyzing academic performance data, attendance and behavior data, standardized test scores, and student survey data, educators can gain valuable insights into their students’ needs and tailor their teaching accordingly.
I have also emphasized the ethical considerations that come with analyzing student data. Protecting student privacy, ensuring data security, and promoting transparency and consent are crucial in maintaining trust and safeguarding the well-being of students.
By prioritizing these ethical considerations, educators can responsibly analyze student data and make informed decisions for the benefit of their students. By using student data effectively, educators can identify areas of improvement, implement targeted interventions, and provide personalized support to help students thrive academically and socially.
Student data analysis is a powerful tool that, when used ethically and responsibly, can greatly enhance educational outcomes and contribute to the overall success of students.